Injection molding has changed the automotive industry by providing a reliable and efficient method for producing a wide range of plastic components. This manufacturing process involves injecting molten plastic into a precisely designed mold, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and high-quality parts. This article explores the significance of injection molding for the auto industry, highlighting its advantages, applications, and key considerations.
Advantages of Injection Molding in Automotive Manufacturing
Injection molding offers numerous benefits that make it a preferred choice for automotive manufacturers:
Cost Efficiency: The initial investment in molds can be high; however, the long-term cost per unit decreases significantly with mass production. Injection molding minimizes material waste, further enhancing cost-effectiveness.
High Production Speed: Modern injection molding machines can produce parts in a matter of seconds. This rapid production capability allows manufacturers to meet the increasing demand for vehicles efficiently.
Design Flexibility: Injection molding supports the creation of intricate designs that would be challenging with other manufacturing methods. This flexibility enables the production of components with complex geometries, such as interior trim and engine parts.
Material Versatility: A wide variety of thermoplastics can be used in injection molding, including polypropylene, ABS, and nylon. This versatility allows manufacturers to select materials that best suit specific applications based on their properties like strength, flexibility, and heat resistance.
Applications of Injection Molding in the Auto Industry
Injection molding is utilized across various automotive applications:
| Application Type | Description |
| Interior Components | Dashboard panels, door handles, and trim pieces are often produced using injection molding for their aesthetic appeal and durability. |
| Engine Components | Parts such as valve covers and intake manifolds benefit from lightweight yet robust plastic materials that withstand high temperatures. |
| Exterior Parts | Bumpers, grilles, and light housings are manufactured to ensure safety and aesthetics while maintaining impact resistance. |
| Electrical Housings | With the rise of electric vehicles, injection molded parts are crucial for battery housings and protective covers for sensitive components. |
Key Considerations in Injection Molding
When utilizing injection molding in automotive manufacturing, several factors must be considered:
Mold Design: The design of the mold is critical to the success of the injection molding process. A well-designed mold minimizes defects and ensures consistent production quality.
Material Selection: Choosing the right material is essential for optimizing performance. Factors such as temperature resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical exposure must be taken into account.
Quality Control: Implementing strict quality control measures throughout the production process is vital to ensure that each part meets industry standards and specifications.
High Quality Injection Molded Auto Parts
FAQs About Injection Molding for Auto Industry
Injection molding is a critical process in the automotive industry, known for its efficiency and ability to produce high-quality plastic parts. Below are some frequently asked questions that provide more insights into this manufacturing technique and its applications in the auto sector.
What types of parts are commonly produced using injection molding in the automotive industry?
Injection molding is used to manufacture a wide range of automotive components, including:
Interior Parts: Dashboard panels, center consoles, door handles, and trim pieces.
Exterior Parts: Bumpers, grilles, fenders, and headlight housings.
Under-the-Hood Components: Intake manifolds, valve covers, and other engine parts.
Electrical Housings: Battery cases and protective covers for sensitive electronic components.
How does injection molding improve production efficiency?
Injection molding enhances production efficiency through several mechanisms:
Rapid Cycle Times: Parts can be produced in seconds, allowing for high-volume production.
Minimal Material Waste: The process is designed to minimize scrap material, leading to cost savings.
Automation Capabilities: Many injection molding processes can be automated, reducing labor costs and increasing consistency.
What materials are typically used in automotive injection molding?
Common materials used in injection molded auto parts include:
Polypropylene (PP): Lightweight and resistant to chemicals; often used for interior components.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Known for its strength and impact resistance; used in dashboards and bumpers.
Polyamide (Nylon): Offers excellent heat resistance; ideal for under-the-hood applications.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): Flexible and durable; suitable for gaskets and hoses.
What are the advantages of using injection molded plastic parts over metal?
Using injection molded plastic parts offers several advantages:
Weight Reduction: Plastic components are generally lighter than metal, contributing to improved fuel efficiency.
Cost Savings: Injection molding can be more cost-effective than metal fabrication due to lower material costs and reduced waste.
Design Flexibility: Injection molding allows for complex shapes that may be difficult or expensive to achieve with metal.
How does the injection molding process work?
The injection molding process involves several key steps:
Mold Design: A precise mold is created based on the desired part specifications.
Material Preparation: Plastic pellets are heated until they melt into a liquid form.
Injection: The molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure.
Cooling: The plastic cools and solidifies within the mold.
Ejection: Once cooled, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected.
What challenges are associated with automotive injection molding?
While injection molding offers many benefits, there are challenges as well:
Mold Design Complexity: Designing molds for intricate parts can be time-consuming and costly.
Material Variability: Different plastics react differently during the molding process, which can lead to defects if not managed properly.
Initial Setup Costs: The upfront investment in molds and machinery can be significant.
Can injection molding be used for prototyping automotive parts?
Yes, injection molding is often used for prototyping automotive parts. Rapid tooling techniques allow manufacturers to create low-cost molds quickly, enabling them to produce prototype parts for testing before full-scale production begins.
How does injection molding ensure quality control in automotive manufacturing?
Quality control in injection molding involves:
Precision Monitoring: Advanced machines monitor critical parameters like temperature and pressure during production to ensure consistency.
Material Testing: Materials are tested for properties such as strength and durability before use.
Post-Molding Inspection: Finished parts undergo inspections to check for defects or deviations from specifications.
Conclusion
The role of injection molding in the auto industry cannot be overstated. Its ability to produce high-quality, cost-effective plastic parts at scale makes it an indispensable process in modern automotive manufacturing. As vehicle designs become increasingly complex and consumer demands continue to rise, injection molding will remain at the forefront of innovation in producing durable and efficient automotive components. By leveraging its advantages, automakers can enhance their production capabilities while meeting stringent quality standards.
With ongoing advancements in technology and materials science, the future of injection molding in the automotive sector looks promising, paving the way for even more innovative solutions in vehicle design and manufacturing.
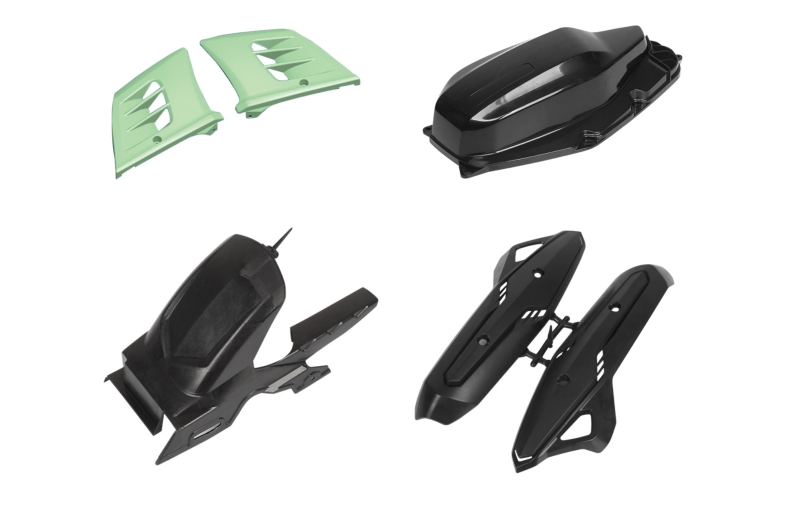


.jpg)

.jpg)